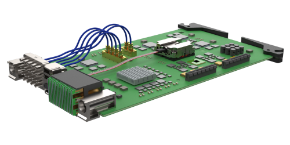
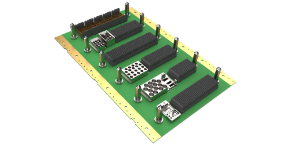
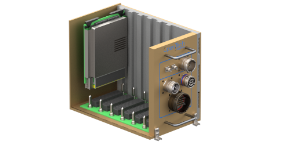
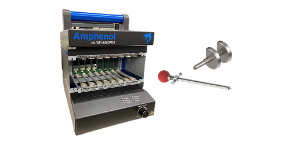
In the realm of aerospace engineering, the VITA 66 standard plays a crucial role in ensuring reliable, high-speed optical connections for space applications. The VITA 66 set of standards encompasses a range of optical modules specifically designed to meet the demanding conditions of space environments. Here, we explore the key considerations for optimizing VITA 66 modules for space applications, focusing on radiation resistance, thermal management, and high-reliability connectors.
VITA 66 Standards
The VITA 66 standard defines blind-mate fiber optic interconnects for use in VPX systems. These modules are designed to support high-density fiber optic connections, which are essential for the high-speed data transfer requirements of space applications. The standard includes several sub-specifications, such as VITA 66.1, 66.2, 66.3, and 66.4, each tailored to different types of optical connectors and their specific applications.
Radiation Resistance
Space environments are characterized by high levels of radiation, which can adversely affect electronic components, including optical fibers. To ensure the longevity and reliability of VITA 66 modules in space, it's essential to select materials and designs that offer robust radiation resistance. Single-mode fibers, for example, are less susceptible to radiation-induced attenuation compared to multi-mode fibers, making them a preferable choice for space applications.
Thermal Management
Thermal management is another critical factor in the design of VITA 66 modules for space. The extreme temperature fluctuations in space can impact the performance of optical interconnects. Implementing effective thermal management solutions, such as heat sinks and advanced thermal interface materials, can mitigate these effects and maintain the integrity of the optical signals. VITA 66 modules often incorporate ruggedized designs to withstand these harsh conditions.
High-Reliability Connectors
The reliability of connectors in space applications cannot be overstated. VITA 66 modules utilize various types of high-reliability connectors, such as MT ferrules and ARINC 801 termini, which offer excellent performance in terms of signal integrity and durability. These connectors are designed to maintain low insertion loss and high return loss, ensuring consistent performance even under the mechanical stresses of space missions.
Modular and Flexible Design
VITA 66 modules are designed with flexibility and modularity in mind, allowing for easy integration and maintenance. This modular approach supports various configurations and upgrades, enabling space systems to adapt to evolving technological requirements without extensive redesigns. The use of blind-mate connectors also facilitates quick and reliable connections, reducing the time and effort required for system assembly and maintenance.
Future Trends and Innovations
As the demand for higher data rates and more robust communication systems in space continues to grow, future developments in VITA 66 technology will likely focus on increasing connector density and improving the performance of optical interconnects. Innovations such as hybrid RF/optical modules and advanced fiber optic technologies will play a pivotal role in meeting these emerging needs.
Conclusion
Optimizing VITA 66 modules for space applications involves addressing several key considerations, including radiation resistance, thermal management, and the use of high-reliability connectors. By focusing on these areas, engineers can ensure that their systems are capable of withstanding the harsh conditions of space while maintaining high performance and reliability. As technology advances, VITA 66 will continue to evolve, offering even more robust solutions for the aerospace industry. Make sure to check out Open.Tech's complete lineup of VITA 66 products for more information.